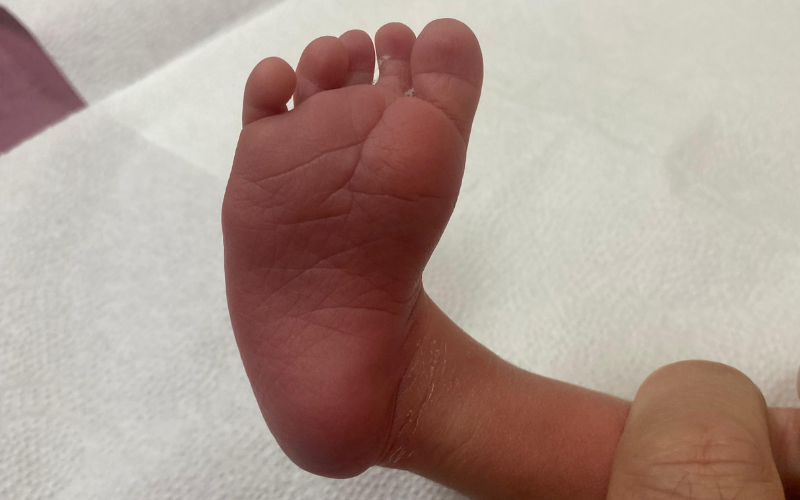
Pes Ekinovarus (PEV)
Pes Equinovarus (Clubfoot)
Pes Equinovarus (PEV), also known as “clubfoot”, is a congenital orthopedic disorder where the feet turn inward and downward. It occurs in 1 to 3 per 1,000 births and can be detected via ultrasound during pregnancy. Diagnosis is confirmed immediately after birth through clinical examination, allowing for early treatment.
What is Pes Equinovarus?
- Affects bones, muscles, and tendons in the foot and ankle.
- The most common congenital foot deformity.
- The foot is positioned inward (varus) and the heel is elevated (equinus).
- Possible causes include genetic factors, intrauterine positioning, and issues in muscle-tendon development.
Diagnosis
- Ultrasound screening can detect clubfoot in the second trimester.
- Physical examination by an orthopedic specialist confirms the diagnosis after birth.
Treatment Methods
- Ponseti Method (Gold Standard):
- The baby’s foot is gradually corrected with serial casting, replaced weekly.
- Treatment typically requires 4-8 cast changes.
- Achilles Tenotomy:
- A minor surgical procedure to lengthen the Achilles tendon if needed.
- Ponseti Brace:
- Used after correction to prevent recurrence.
Parental Involvement and Follow-up
- Regular medical check-ups are crucial.
- Proper cast and brace care ensures successful outcomes.
- Physical comfort and skin health monitoring are essential.
- Children treated early can walk and run normally like their peers.
Early diagnosis and correct treatment can ensure a healthy, active future for children with Pes Equinovarus. Families should seek consultation with a pediatric orthopedic specialist if they suspect clubfoot.